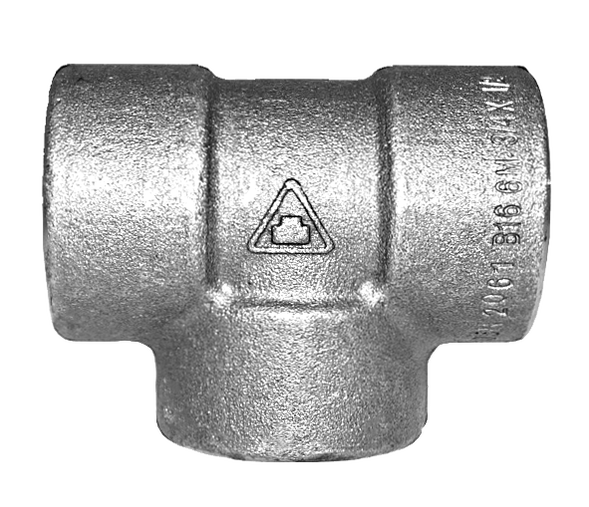
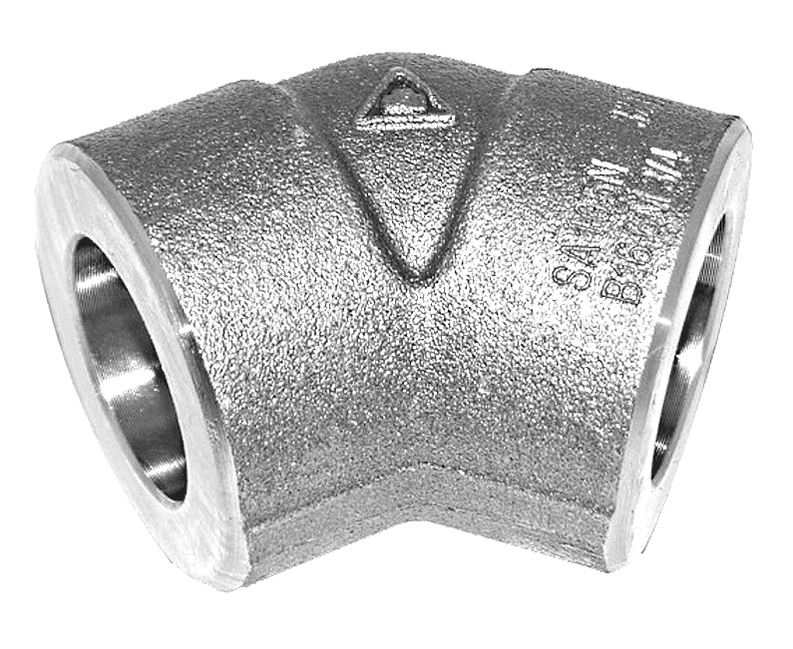
Forged Pipe Fittings
Forged pipe fittings are made according to ASME B16.11, MSS-SP-79\83\95\97 and BS3799 standards. It is a connector in between nominal bore pipes. The fittings are made of carbon steel A105 and stainless steel SS316 material. The size available is from 1/8” to 4”
Forged pipe fittings was named via its manufacturing forging process, which was to heat alloy steel or carbon in a transforming temperature and moulds the heated parts into their customizable shape. The common brand is Both-well, Taiwan.
Forged pipe fittings was named via its manufacturing forging process, which was to heat alloy steel or carbon in a transforming temperature and moulds the heated parts into their customizable shape. The common brand is Both-well, Taiwan.
Size |
|
Material Specification |
|
Class Pressure |
|
Connection Type |
|
What are Forged Pipe Fittings
1. What are forged pipe fittings used for?
|
A forged pipe fitting has a high quality as it has higher strength to withstand higher pressure. The wall thickness is thicker than other type of fittings for threading process or machining to socket weld end.
The standard of ASME B16.11 contains pressure-temperature ratings, tolerances, dimensions, markings and material requirements for forged pipe fittings. It is used in chemical, power generation and oil & gas industry where high pressure or extremely corrosive conditions exist. |
2. How are forged pipe fitting made?
Each forged pipe fitting will be permanently marked with the required identification by engraving marking on the collar portion. The purpose is to keep user at ease when identifying the specification and ensure system are running smoothly. The marking shall include:
Each forged pipe fitting will be permanently marked with the required identification by engraving marking on the collar portion. The purpose is to keep user at ease when identifying the specification and ensure system are running smoothly. The marking shall include:
The class pressure 3000 and 6000 will label as 3M or 6M, where M means by 1000. 3M is referring to 3000 lbs fittings, which the forged pipe fitting can withstand up to 3000 PSI or 206 Bars. Material Identification of A105 shall not be marked as carbon steel material is group under standard material grade. Other material such as SS316 material will clearly stamp on the fitting body.
3. What does 3m and 6m mean on forged pipe fittings?
Forged pipe fitting designed as pressure class 2000, 3000, 6000 and 9000. The most common pressure class to use in application is class 3000 and 6000. Please check different of 3M and 6M pipe fittings below:
Forged pipe fitting designed as pressure class 2000, 3000, 6000 and 9000. The most common pressure class to use in application is class 3000 and 6000. Please check different of 3M and 6M pipe fittings below:
Description |
3000 PSI (3M) |
6000 PSI (6M) |
Body Size |
Smaller |
Bigger |
Thickness |
Thinner |
Thicker |
Unit Weight |
Lighter |
Heavier |
Working Pressure |
Lower |
Higher |
4. What are different types of forged pipe fittings?
There are variety fittings type to choose when comes to system customize. They are 90D elbow, 45D elbow, straight coupling, 3 piece union, 3 way tee, end cap, end plug, hex nipple and etc.
3 Way tee comes in T-shape and it has one inlet and two outlets. It used to combine the flow from two inlets to one outlet. Reducer is the component which helps to reduce the flow size from larger to smaller. Hex bush is another component to help in enlarges the flow from smaller to larger size.
There are variety fittings type to choose when comes to system customize. They are 90D elbow, 45D elbow, straight coupling, 3 piece union, 3 way tee, end cap, end plug, hex nipple and etc.
3 Way tee comes in T-shape and it has one inlet and two outlets. It used to combine the flow from two inlets to one outlet. Reducer is the component which helps to reduce the flow size from larger to smaller. Hex bush is another component to help in enlarges the flow from smaller to larger size.
No |
Type of Forged Pipe Fittings |
Connection |
1 |
Straight Coupling |
Female x Female |
2 |
90D / 45D Elbow |
Female x Female |
3 |
3 Way Tee |
Female x Female x Female |
4 |
3 Piece Union |
Female x Female |
5 |
End Cap |
Female |
6 |
90D / 45D Street Elbow |
Female x Male |
7 |
Hex Plug |
Male |
8 |
Hex Nipple |
Male x Male |
9 |
Hex Bush |
Female x Male |
10 |
Half Coupling |
Female |
5. How do you join a threaded pipe?
The connection can be threaded or socket weld end. NPT thread is the most common connection in installation as the tapered thread help make better seals. The female and male both threads compress and wedge themselves together. While BSP parallel thread is available too for certain straight regular connection such as full coupling, hex nipple and hex plug. Male threaded pipe end is needed if the threaded fittings are used for system installation.
The connection can be threaded or socket weld end. NPT thread is the most common connection in installation as the tapered thread help make better seals. The female and male both threads compress and wedge themselves together. While BSP parallel thread is available too for certain straight regular connection such as full coupling, hex nipple and hex plug. Male threaded pipe end is needed if the threaded fittings are used for system installation.
|
Alternatively, welding is the simpler way to join both fitting and pipe together. The plain end pipe will insert into a recessed area of fittings before start welding. Standard fitting have the same connection for all end connection. However, there are some customise project may need special fitting design, example: one threaded end and one socket weld full coupling fittings. It can be machine upon request.
When the fitting connects to pipe, the schedule pipe corresponding to each pressure class of fittings to create an efficient system application at the maximum material resources supplied. |
Pressure Class |
Connection |
Pipe Schedule |
3000lb |
Threaded |
SCH 160 |
6000lb |
Threaded |
SCH XXS |
3000lb |
Socket Welding |
SCH 80 |
6000lb |
Socket Welding |
SCH 160 |
The table is a reference of pipe schedule thickness and it is not compulsory to restrict the pipe schedule and fittings class pressure. Calculation of minimum pipe wall thickness shall include application pressure design and all applicable additional factors such as corrosion, threaded depth, surrounding temperature and environment factor.