Gate Valves
|
|
|
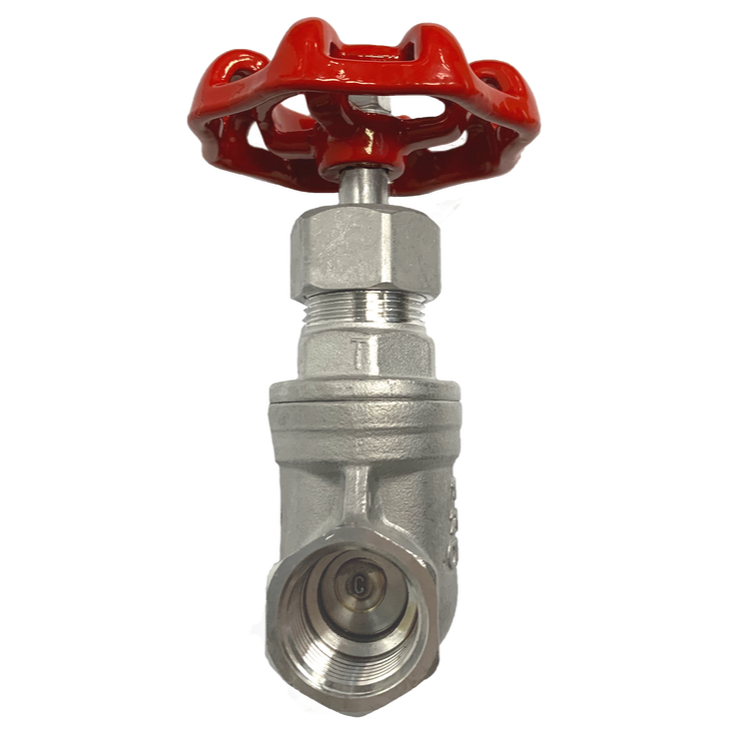
Gate valve is a valve designed to fully open or fully close by using a gate or wedge type disc. The purpose is mainly for blocking fluid flow. The disk moves perpendicular to the flow while fluids start and stop in the piping system.
It requires very little space along the pipe axis for gate valve to restrict the flow of fluid. Gate valve operation performs in either clockwise to open (CTO) or clockwise to close (CTC) rotating motion of the stem and hand wheel. Main components of a gate valve are its body, seat, wedge, stem, gasket, hand wheel and bonnet.
It requires very little space along the pipe axis for gate valve to restrict the flow of fluid. Gate valve operation performs in either clockwise to open (CTO) or clockwise to close (CTC) rotating motion of the stem and hand wheel. Main components of a gate valve are its body, seat, wedge, stem, gasket, hand wheel and bonnet.
Size |
|
Material |
|
Working Pressure |
|
Connection Type |
|
CATALOGUE :
Product Specifications
For more information on the individual product specifications, please click on the links below:
What are gate valves
1. How do gate valves work?
|
The main purpose of gate valve is to shut off the flow of fluids in a system. The valve is designed to be in either a fully opened or fully closed position. It is suitable to apply in low pressure application and the pressure rating can be up to 150 PSI working pressure. The valve operates with a wedge or disc in the middle and it prevents flow of the fluid process to flow through the valve body. The wedge or a disc lifting up and down by rotating the wheel handle according to label “open” and “close” on the handle.
A gate valve is a multi-turn valve meaning that the valve operation can be done by threaded stem. The valve has to turn multiple times from open to close position, so that the slow operation prevents water hammer effects. The gate moves up or downwards on the threaded stem part when operating the valve stem. Gate valve can be applied in all fluid services such as fuel gas, air, feed water, steam, hydrocarbon and lube oil. |
2. What is a gate valve used for?
A gate valve is the most commonly used for process plant application as it is a linear motion valve used to control the fluid flow. The valve can be either in fully opened or fully close position. The gate valve disc is completely removed from the flow when the gate valve is at fully opened position. A typical gate valve has no blocking in the flow path. Thus, resulting in a very low pressure loss and a free bore is created. When the valve is fully closed, a 360° surface contact is required between the disc and seats in order to perform proper sealing.
It is not applicable as control or regulating valves due to the accuracy of flow control is not achievable. The high velocity of the flow in the partially opened valve is not encouraged. It may cause erosion to the seating surface and disc which will next lead to vibration and noise.
There are different types of body gate valve as per below:
A gate valve is the most commonly used for process plant application as it is a linear motion valve used to control the fluid flow. The valve can be either in fully opened or fully close position. The gate valve disc is completely removed from the flow when the gate valve is at fully opened position. A typical gate valve has no blocking in the flow path. Thus, resulting in a very low pressure loss and a free bore is created. When the valve is fully closed, a 360° surface contact is required between the disc and seats in order to perform proper sealing.
It is not applicable as control or regulating valves due to the accuracy of flow control is not achievable. The high velocity of the flow in the partially opened valve is not encouraged. It may cause erosion to the seating surface and disc which will next lead to vibration and noise.
There are different types of body gate valve as per below:
|
1. Type of body bonnet joint
1.1 Screwed bonnet 1.2 Bolted bonnet 1.3 Welded bonnet 1.4 Pressure sealed bonnet 2. Type of disc 2.1 Solid taper wedge 2.2 Flexible wedge 2.3 Split wedge or parallel disc valve 3. Types of stem movement 3.1 Rising stem or OS & Y type (Screw end type & outside stem) 3.2 Non-rising stem type |
3. What is a bonnet on a valve?
Type of Body Bonnet Joint |
Features |
Screwed bonnet |
|
Bolted bonnet |
|
Welded bonnet |
|
Pressure sealed bonnet |
|
4. What are different types of gate valves?
- Solid taper wedge: The most common and widely used disc type gate valve because of its strength and simplicity. A valve with solid wedge can be installed in any position and it is suitable for all type of fluids. However, it does not compensate in aligning to changes in seat alignment due to pipe loads or thermal expansion. The disc design is most susceptible to leakage. For application under high temperature service, solid wedge is subjected to thermal locking. Thermal locking is a phenomenon in which wedge is stuck between the seats and cause the expansion of the metal. Solid wedge type gate valve are commonly used in moderate to lower pressure temperature application.
- Flexible wedge: One piece of solid disc with a cut around the perimeter. This cut varies in size, depth and shape. A shallow, narrow cut on wedge perimeter gives strength retains and less flexibility. A cast-in recess or a wider and deeper cut on the wedge perimeter gives more flexibility. This type offers better leak tightness and improves seat alignment. It improves performance in situations such as thermal binding. Thermal binding is a phenomenon in which the wedge is jammed in the close position. The primary causes are a relatively cool valve stem is inserted into a hot valve and the stem warm up and grow further increasing the seating force after closing on torque. As the valve body cool down, the seats contact on the valve wedges locking them in place. Flexible wedges are commonly used in steam system application. The disadvantage of flexible wedge is that line fluid tends to gather in the disc and result in corrosion and ultimately weaken the disc.
|
5. What is rising stem gate valve?
Gate valve designed in rising stem and non-rising stem type. Rising stem gate valve is able to trace open or close position by moving the stem up & down movement and the stem will go up while valve is at opening position. It would move down when the valve is closed. It provides a visual indication of the valve position and making it possible to grease the stem.
This valve type is suitable for above ground installation only and the nut rotates around the threaded stem and moves it. The valve is closed when the stem is not visible above the control wheel and the valve is open when the threaded stem extends from top of the wheel. This called OS & Y valve, mean that outside steam and yoke or outside screw and yoke.
Gate valve designed in rising stem and non-rising stem type. Rising stem gate valve is able to trace open or close position by moving the stem up & down movement and the stem will go up while valve is at opening position. It would move down when the valve is closed. It provides a visual indication of the valve position and making it possible to grease the stem.
This valve type is suitable for above ground installation only and the nut rotates around the threaded stem and moves it. The valve is closed when the stem is not visible above the control wheel and the valve is open when the threaded stem extends from top of the wheel. This called OS & Y valve, mean that outside steam and yoke or outside screw and yoke.
|
Non-rising stem type performs no upward movement of the stem. The disc is threaded internally and travels along the stem when the wheel turning and steam rotates. The steam threads are exposed to the flow medium and the valve design is used where space is limited to allow linear steam movement. The flow medium does not cause corrosion or erosion.
The main difference between rising and non-rising stem gate valve is the appearance of the rising stem gate valve can be seen from the appearance to check the valve is close or open position. The lead of stem is the part to identify. |
6. What is resilient seated gate valve?
Metal seated wedge were widely used before resilient seated gate valve was introduces to the market. The metal seated wedge angular sealing devices and conical wedge valve design requires a depression in valve bottom to ensure the valve is at tight closing position. Some sand and pebbles are embedded in the bore. Regardless of how thoroughly the pipe is flushed upon installation or maintenance, the pipe system installation will not be completely free from impurities Therefore, any metal wedge will eventually lose its ability to be drop-tight and create inefficient installation.
A resilient seated gate valve allows free passage for pebbles and sand in the valve body cause it has a plain or flat valve bottom. The rubber surface will close around the impurities at valve closing position if impurities pass as the valve closed. A high quality rubber element compound absorbs the impurities as the valve closes. When the valve opened again, the impurities will be flushed away. The rubber surface will attain its original shape securing a drop-tight sealing.
Metal seated wedge were widely used before resilient seated gate valve was introduces to the market. The metal seated wedge angular sealing devices and conical wedge valve design requires a depression in valve bottom to ensure the valve is at tight closing position. Some sand and pebbles are embedded in the bore. Regardless of how thoroughly the pipe is flushed upon installation or maintenance, the pipe system installation will not be completely free from impurities Therefore, any metal wedge will eventually lose its ability to be drop-tight and create inefficient installation.
A resilient seated gate valve allows free passage for pebbles and sand in the valve body cause it has a plain or flat valve bottom. The rubber surface will close around the impurities at valve closing position if impurities pass as the valve closed. A high quality rubber element compound absorbs the impurities as the valve closes. When the valve opened again, the impurities will be flushed away. The rubber surface will attain its original shape securing a drop-tight sealing.
7. What is the difference between a gate valve and a ball valve?
|
Ball valve and gate valve is two most common valves for controlling the fluid flow in plumbing or gas systems. Ball valve is effective at forming a tight seal and has more reliability and longevity than gate valve and usually the cost is higher. They are often applying in shutoff and control flow application. While gate valve has an internal disc or wedge to allow flow process and the cost is slightly lower. They are often applying in larger pipe diameters of 2” and above.
Ball valve can open and close immediately and when come to gate valve, it would cause water hammer. When a valve is closed quickly on water moving at high pressure through pipes, it would cause shock waves through the system that create a hammering sound. |
If system is running in high pressure application, water hammer causes a pipe move and strike against one another. The net pressure of the system isn’t increased significantly and some pipe pressure is far below pipes working pressure capacity, which in turn to safety factor. Serious problems can cause to pipe broken and system damage. Both ball and gate valve provides similar functions while offering different level of flow control.
Kindly take note criteria below before you choose the correct valve design:
Kindly take note criteria below before you choose the correct valve design:
- Application type
- Valve flow design
- Material
- Cost application
8. Why do gate valves fail?
|
Gates valve comes with middle disc that moves when the valve handle turn on to control the flow of fluid. As the valve ages, the disc tends to stick and when the valve is at fully close position, the water will flow through due to the disc has stuck in opening position. The disc may remain stuck in the closing position when the handle turns back to open position. Therefore, the dysfunction gate valve did not serve the purpose of gate valve.
The most common cause of gate valve failure is wear and corrosion as it tends to wear out all the time. Corrosion would cause the disc to tick in either the closing or open position. When the handle is force to turn, the stem leading from the handle to the disc will often break and cause the valve damage. |
CATALOGUE :